Copper ore is typically a mixture of copper sulfide or oxide and other minerals.
Copper has the second highest conductivity after silver, and it is more abundant and affordable than silver.
As a crucial material in the high-tech industry, copper holds significant economic value.
Additionally, copper ore processing plants yield substantial returns on investment profits.

Copper industrial minerals include natural copper, chalcopyrite, chalcocite, tetrahedrite, azurite, malachite, and more. Chalcopyrite is the primary compound mined, followed by chalcocite and bornite.
To fully utilize copper ore, it must undergo flotation processing. Flotation separation is a crucial process in the current mineral beneficiation market for copper ore. By understanding the characteristics of the ore, we can tailor a suitable processing plant and equipment.
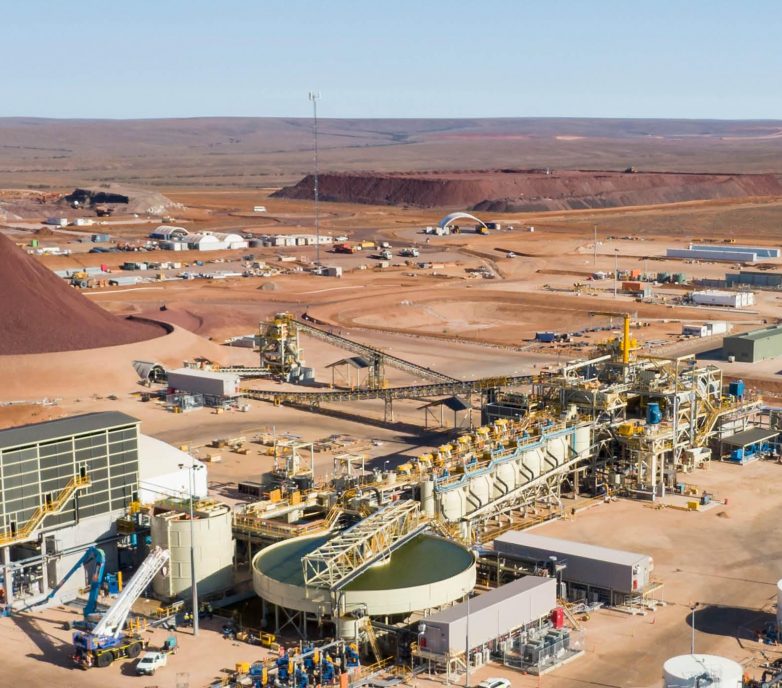
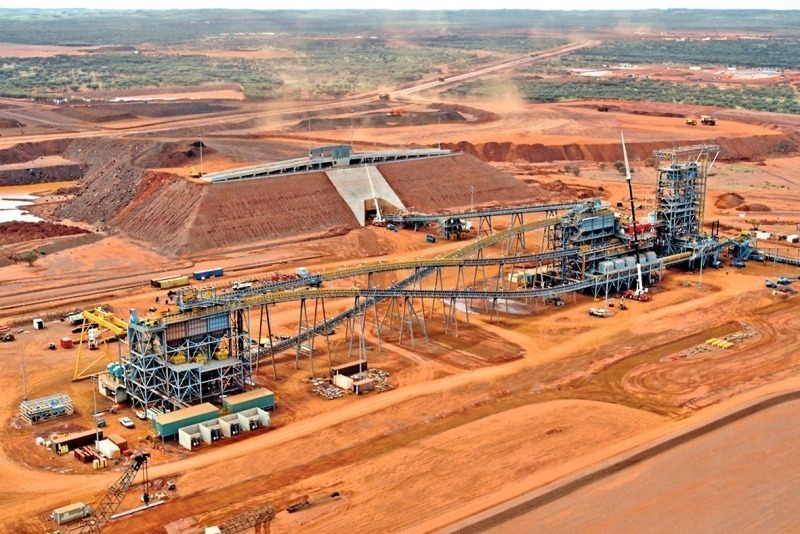
Copper Concentrate Processing Plant
Copper ore is categorized into sulfide ore, oxide ore, and mixed ore based on its oxidation rate. The primary technological process for copper ore is flotation. For refractory mixed copper ore and refractory oxide ore, the hydrometallurgical process is generally utilized.
The beneficiation process of copper ore relies on the physical and chemical properties of different minerals present in the copper ore. After crushing and grinding the ore, various beneficiation processes such as gravity separation, flotation, magnetic separation, electric separation are employed to separate valuable minerals from gangue minerals while keeping associated useful minerals separated from each other as much as possible. This process aims to remove or reduce harmful impurities in order to obtain raw materials suitable for smelting or other industries.
Flow of Copper Processing Plant
A single sulfide ore is typically treated using a flotation process that involves crushing-grinding-classification-flotation-concentration steps to produce a single copper sulfide concentrate.
In the priority flotation process for copper ore beneficiation, the principle follows: crushing and screening → grinding and classification → priority flotation of copper concentrate → activation flotation of other concentrates → concentration and dehydration.
In the mixed flotation process for copper ore beneficiation, the principle follows: grinding and classification → obtaining mixed concentrate through mixed flotation → separating and rough concentrating the concentrate → concentration and dehydration.
The positive flotation process for copper ores includes: crushing and screening, grinding and grading, roughing selection
Preparation process prior to separation
This process includes crushing, screening, grinding, grading, and other procedures for copper ore.
The objective of this process is to separate valuable minerals from gangue mineral monomers and dissociate various useful minerals from each other.
1. Crushing procedure
The copper ore that requires processing must first undergo the crushing procedure. The vibrating feeder feeds through the silo and evenly sends the material to the jaw crusher for primary crushing. The large raw ore is then broken into smaller pieces of ore. After coarse crushing, the crushed copper ore goes through screening and is sent to the cone crusher via a belt conveyor for intermediate and fine crushing until it becomes smaller particles.
2. Grinding procedure
The granulated copper ore is screened by a vibrating sieve before being sent to a ball mill for grinding and crushing. An auxiliary equipment called a classifier is also needed here. It classifies and screens the copper ore, releasing copper powder that meets requirements.
3. Screening and classification
Based on sieve surface size, materials are divided into different particle size grades which are often used for coarser materials processing purposes. By considering different settling speeds of particles in medium (usually water), materials are divided into equal-fall grades known as classification; this method applies to smaller particle sizes materials selection purposes as well.Screening and grading aim at separating suitable particle-sized materials during the crushing process or dividing them into different particle size grades for individual selection.
4. Flotation Process
Flotation is a commonly used beneficiation method for copper ore due to the good floatability of most copper minerals. The ground copper ore powder is sent to the flotation machine, where it reacts with various chemical solvents added in the machine. The flotation machine separates the copper ore from gangue and other attached metal minerals based on their hydrophilicity and other characteristics.
Concentrates and Tailings Processes
This includes dehydration, precipitation concentration, filtration, drying, washing, and clarification of fine-grained materials in various copper concentrates and tailings products.
Most copper ore beneficiation products contain a significant amount of water, which hinders transportation and smelting processing. Therefore, it is necessary to remove moisture from the beneficiation products before smelting.
Copper Flotation Machine
The copper ore flotation machine is the main equipment used in the beneficiation processing of copper ore, which generally adopts a flotation production line.
Designed with multi-stage separation tanks, the copper ore flotation machine gradually completes the entire flotation process, optimizing it in a cascading manner. This design accommodates the changing properties of materials in different sections and enhances separation accuracy.
The copper ore powder flotation machine ensures better stability for refractory and complex copper ores or high-grade concentrates. It also minimizes equipment wear, reduces energy consumption, and lowers investment costs during the flotation process.
1) Copper concentrate concentration involves using gravity or centrifugal force to precipitate solid particles in the beneficiation products. Concentration is usually carried out in a thickener to remove some of the moisture.
2) Copper concentrate filtration achieves solid-liquid separation by passing the ore slurry through a water-permeable and impermeable spacer layer of solid particles. Filtration is performed after concentration as an additional dehydration step typically using a filter.
3) Copper concentrate drying is the final stage of dehydration. It reduces moisture through heating and evaporation but is only necessary when further drying of dewatered concentrate is required. Drying operations are generally conducted in dryers or other similar devices.
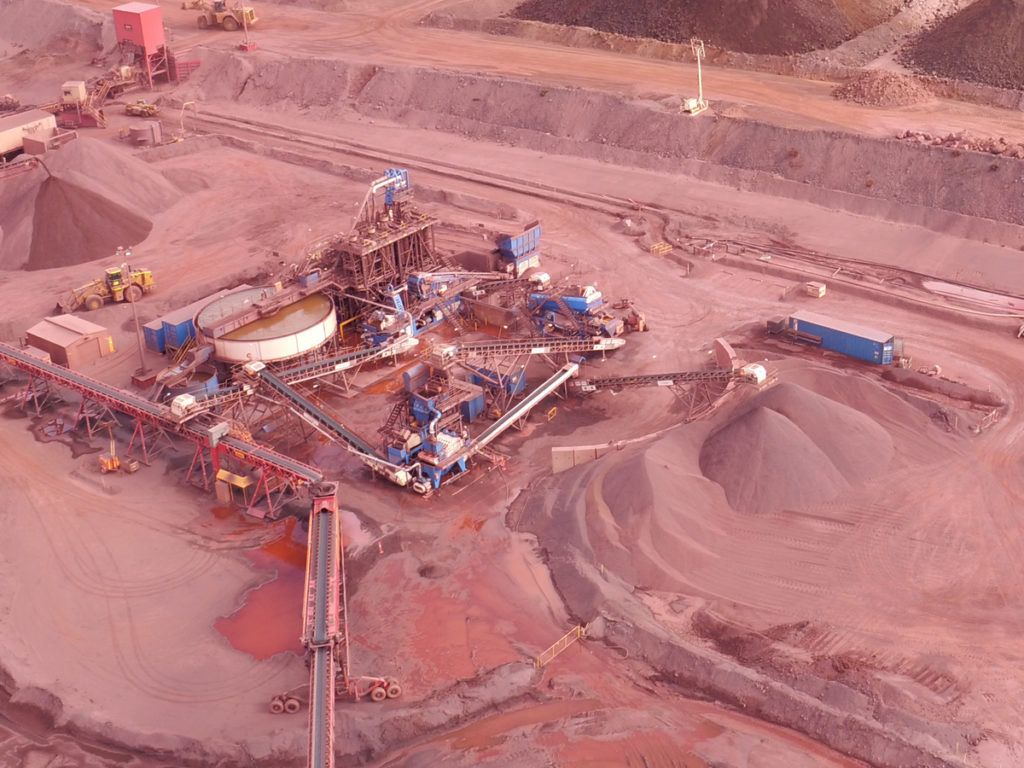
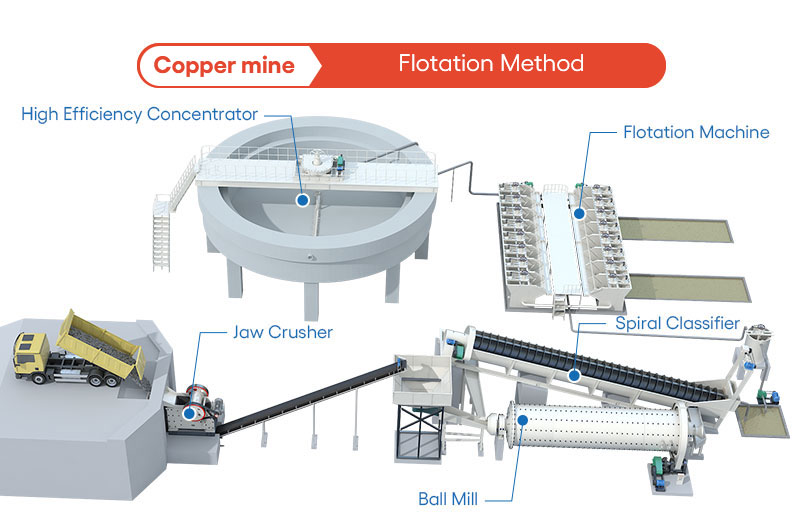

Copper Mine Concentrate Processing Plant
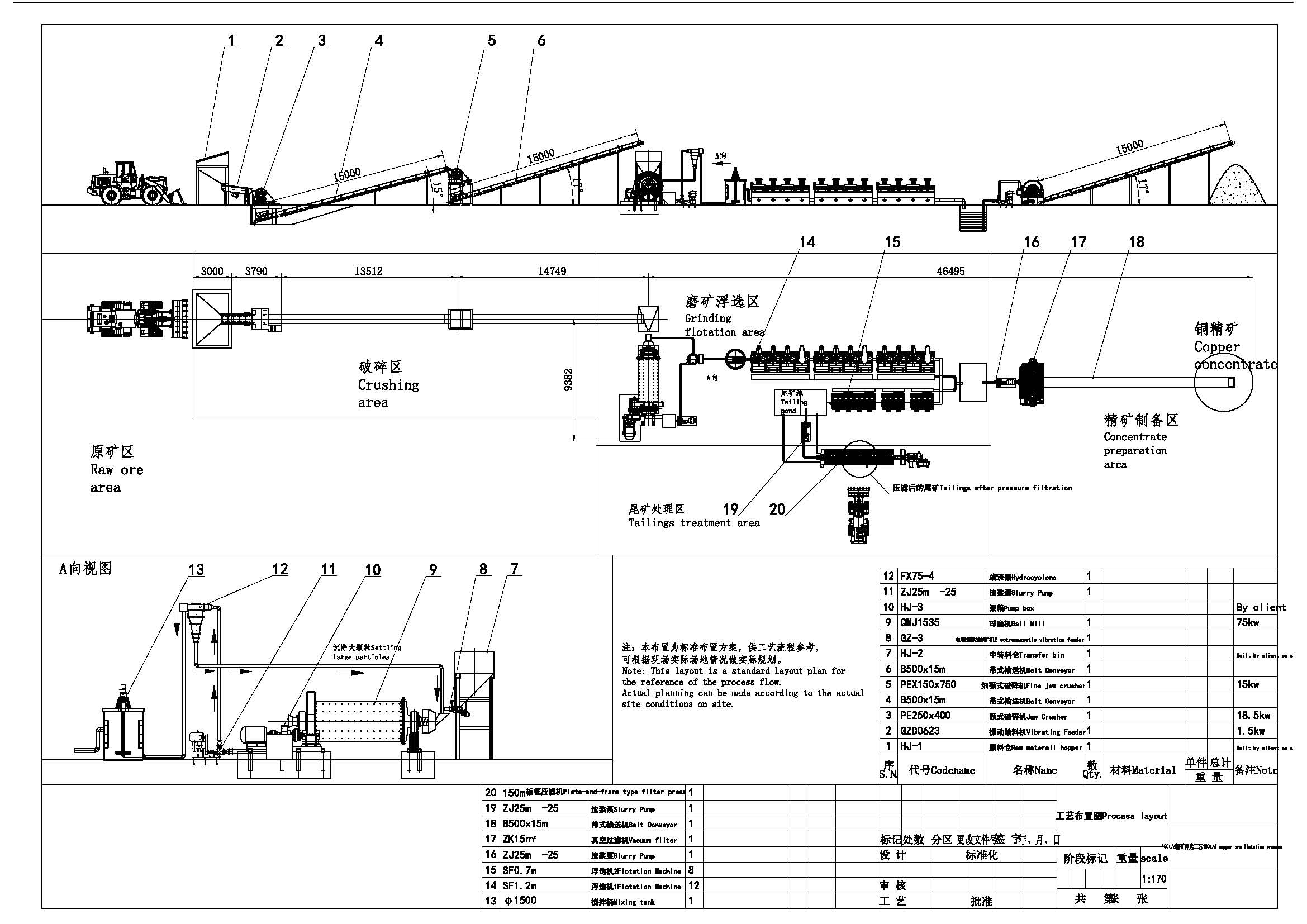
If you are interested in ordering, please contact us