Are you familiar with tantalum-niobium ore? It can be found in your phone, laptop, computer, and TV.
Tantalum-niobium ore is a broad term used to describe minerals that contain tantalum and niobium, typically in the form of coltan (columbite-tantalite). Tantalum and niobium are classified as “rare metals”.

Tantalum and niobium, which are always found together, are listed on both the U.S. 2022 critical minerals list and the EU critical raw materials list.
Niobium and tantalum have a close symbiotic relationship, sharing many similar physical properties. They are commonly found in tantalite-columbite minerals within pegmatites, granites, and alkaline igneous rocks.
The beneficiation of tantalum-niobium ore is primarily determined by the properties of the raw ore. Here are some physical properties of minerals from the tantalite-columbite series:

Composition: Tantalum-niobium minerals consist of both tantalum (Ta) and niobium (Nb) elements.
Color: The color of tantalum-niobium ore varies, usually appearing black, tan, brown, or reddish-brown.
Hardness: With a Mohs hardness ranging from 6 to 6.5, they are resistant to wear and can endure mechanical stress.
Luster: Tantalum-niobium minerals exhibit a metallic or sub-metallic luster with a shiny appearance.
Magnetism: Due to the presence of iron in their crystal structure, particularly columbite, they possess weak magnetic properties.
Density: These minerals have relatively high density values typically ranging from 5.8-8.2 g/cm3. This high density facilitates easy separation by gravity.
There are 10 types of industrial mineral raw materials for niobium and tantalum, but the main mined ores are the following 3:
Tantalite: Contains Ta2O5>72.18%, Nb2O5<10.33%
Columbite: Contains Ta2O5<14.55%, Nb2O5>63.77%
Pyrochlore: Ta2O5 content is 1.44%-6.65%, and Nb2O5 is 56.01%-67.77%
The history of coltan mining
How is coltan mined? Its mining process is quite primitive, similar to gold mining in California in the 1800s. Miners extract the ore by hand, then pan and filter rock and sand until the minerals settle at the bottom.

Small-scale artisanal mining is prevalent in certain regions of Africa and can give rise to environmental and safety issues. As times progress, there is an increasing demand for mining equipment.
Tantalum-niobium ore beneficiation process
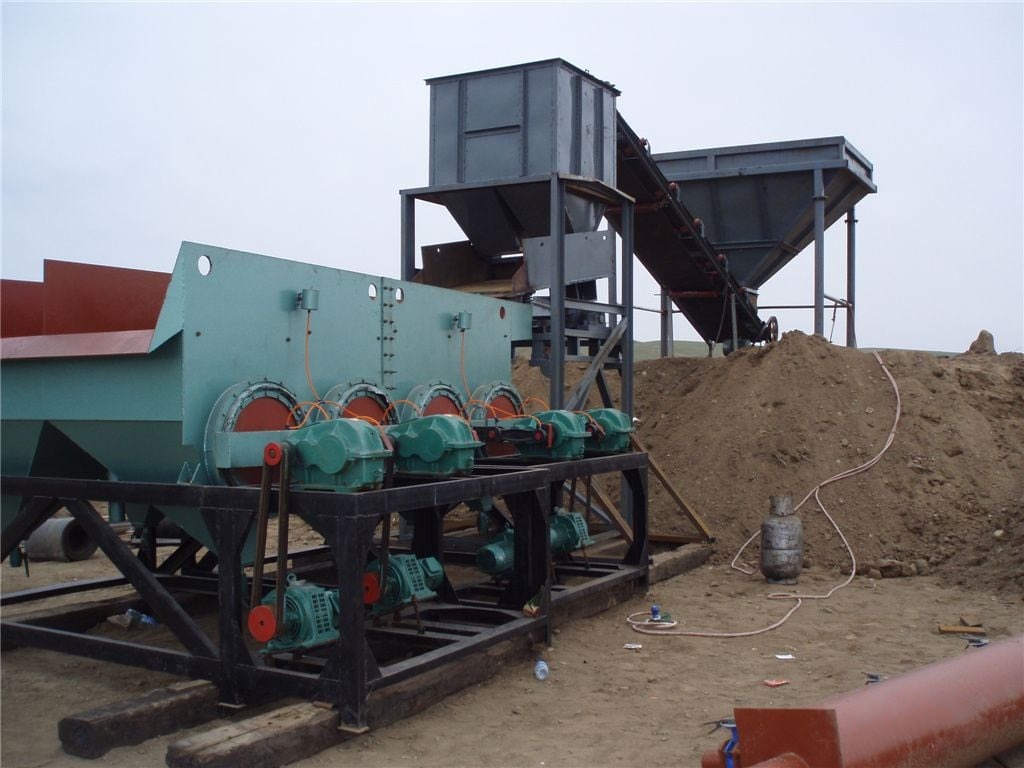
Stage 1: Crushing and grinding
Tantalite and columbite ores are brittle, making it relatively easy to separate the mineral monomers. The extracted tantalum-niobium ore is initially crushed using a hammer crusher, reducing it to as small as 25 mm.
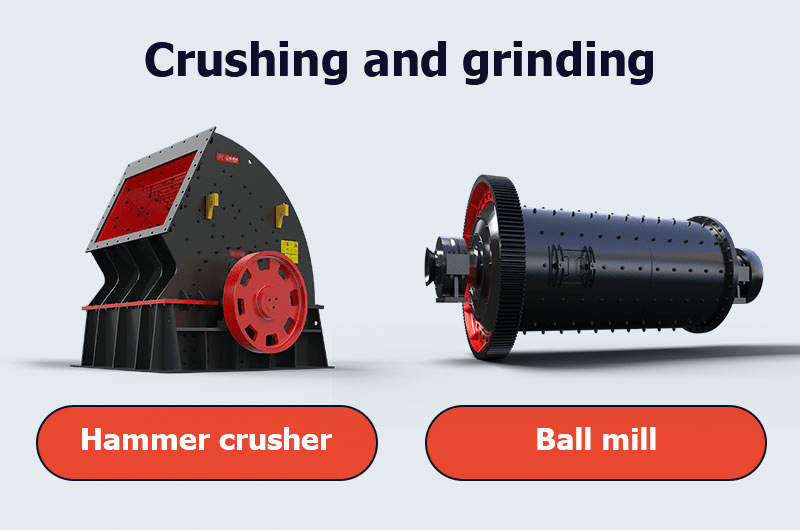
Once the ore is crushed to an appropriate size, it is then uniformly fed into a ball mill through an ore feeder for further crushing and grinding. This process aids in liberating valuable minerals (such as tantalum and niobium) from the gangue material.
Stage 2: Washing and grading
Tantalum-niobium ore typically has a high mud content, with even placer mines exceeding 70% mud. When dealing with highly viscous clay, it is crucial to carry out ore washing operations.
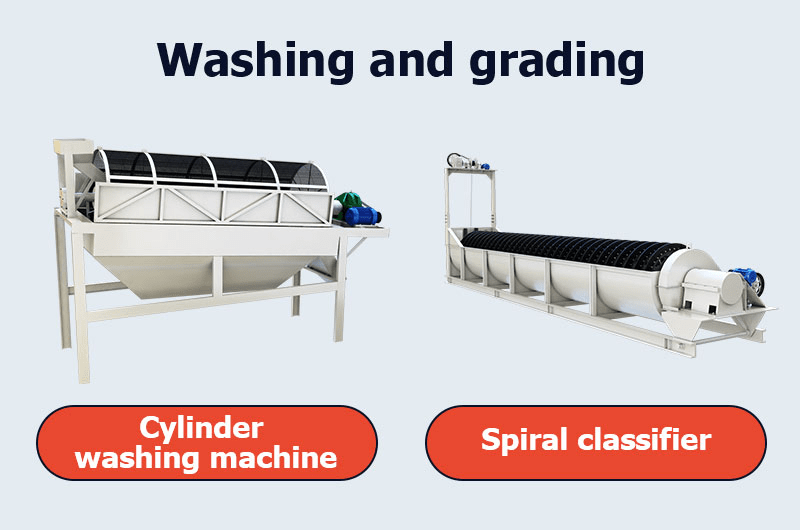
The raw ore is initially deslimed in the cylinder washing machine. Then, the tantalum-niobium ore fines are cleaned and classified in a spiral classifier. After two washes, the mud content in the raw material is reduced to less than 2%.
Stage 3: Multi-stage beneficiation
Tantalite-niobium ore consists mainly of polymetallic ores containing tantalum, niobium, tin, tungsten, lithium, and beryllium. It is characterized by a low grade of raw ore and a complex mineral composition. The mineral processing process is typically divided into rough separation and concentration stages.
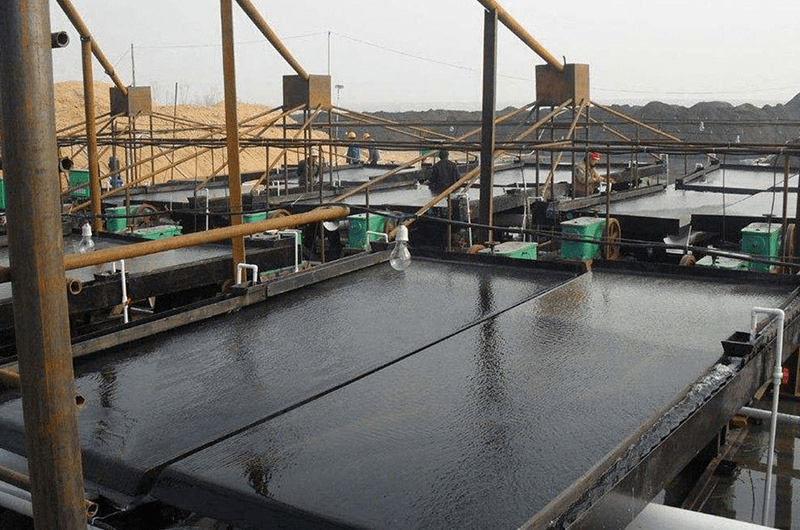
① Roughing separation of tantalum niobium ore – gravity separation method

Currently, gravity separation is the most important method for processing tantalum-niobium ore, particularly for beneficiation of tantalum-niobium sand ore found on seashores, riversides, and sandy beaches. The raw ore contains valuable metals like columbite, tantalite, cassiterite, zircon sand, ilmenite, etc., which have significant differences in specific gravity.
To achieve higher purity levels in separating tantalum-niobium ore, a spiral chute is commonly employed. Initially, most of the gangue minerals are discarded to obtain a low-grade mixed coarse concentrate. Subsequently, a shaking table is used to separate the concentrate or tailings and yield various products.
② Cleaning separation of tantalum niobium ore – magnetic separation, flotation, combined process
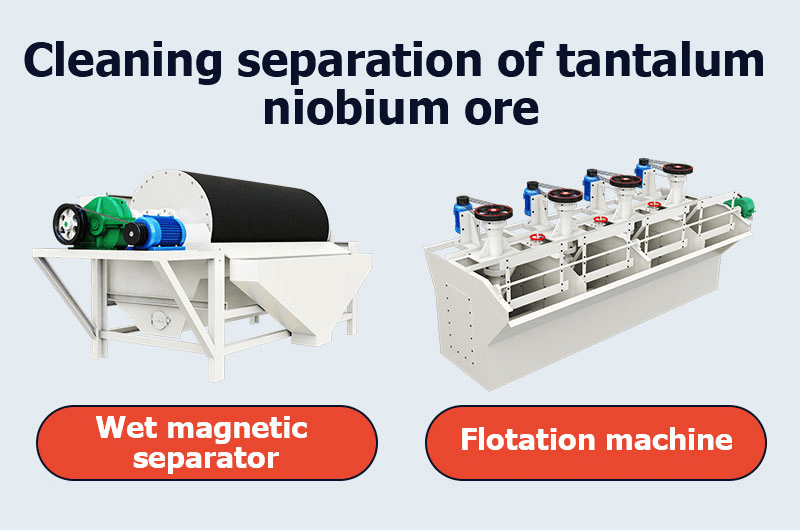
Tantalite and columbite are naturally magnetic minerals due to their iron content, making them suitable for gravity-magnetic separation. A wet magnetic separator is more effective than a dry one in separating tantalum, niobium, and non-magnetic minerals while improving the concentrate grade.
For fine-grained tantalum-niobium ore with fine mud that is difficult to sort, gravity separation-flotation is mainly used. Commonly used collectors for flotation include fatty acids, arsenic acids, cationic collectors, etc. Although the flotation method has a high separation index, it requires a large amount of chemicals and incurs high costs.
Where is tantalum-niobium ore found?
Tantalum and niobium deposits can be found in many countries worldwide. Some countries with significant historical mining or concentration activities include:
- The Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC): Congo is one of the largest producers of tantalum-niobium ore, with abundant reserves in its eastern region.
- Rwanda: Another important producer of tantalum-niobium ore on the African continent.
- Nigeria: Coltan deposits are often found in association with tin mining operations in Nigeria.
- Australia: Western Australia is a major producer of tantalum concentrate.
- Brazil: Brazil holds the title for being the world’s largest producer and miner of niobium.
- Canada: Pegmatite deposits in Canada frequently contain tantalum and niobium minerals.
The Democratic Republic of Congo and Rwanda together account for over half of global tantalum production. Meanwhile, Brazil’s annual niobium production represents 88% of the world’s total output. Let’s now delve into specific solutions from Congo and Brazil.
Guogao tantalum-niobium ore solutions

GUOGAO provides equipment
| Machine | Model | Quantity |
| Trommel screen | YTS2040 | 1 |
| Shaking table | 6-S type | 2 |
| Magnetic separator | CTB1024 | 1 |
| Belt conveyor | TD75 type | 4 |
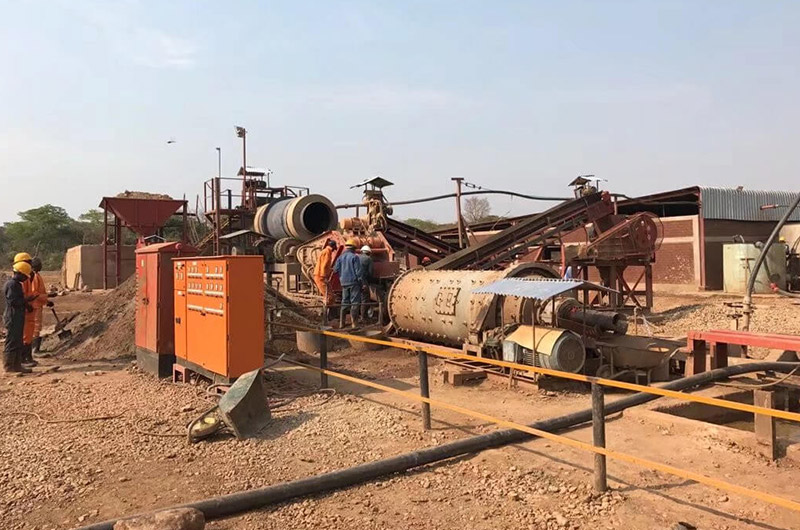
100 TPH tantalum-niobium ore beneficiation:
Tantalum, niobium, and zirconium mine plant in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC).
In a large granite-type deposit in Brazil, the main valuable minerals are tantalite, columbite, zircon, and monazite. These minerals are fine-grained and closely associated with plagioclase, quartz, and mica. They also exhibit poor dissociation properties.
Obtaining high-quality tantalum, niobium, and zirconium products through gravity separation of raw ore is challenging due to low recovery rates. However, using mixed flotation can significantly enhance overall recovery rate.

| Machine | Model | Quantity |
| Hammer crusher | PCZ1308 | 1 |
| Ball mill | Ф2700×4000 | 1 |
| Trommel screen | YTS1550 | 1 |
| Shaking table | 6-S type | 2 |
| Flotation machine | KYF-24 | 2 |
| Belt conveyor | TD75 type | 6 |
The customer ultimately processed the ore using the method of “crushing – fine grinding – desliming – gravity separation – mixed flotation of tantalum, niobium, and zirconium” to obtain mixed concentrates of tantalum, niobium, and zirconium.
CONGO mineral processing plant information
| Mineral | Nb2O5 | ZrO2 | Ta2O5 |
| Raw ore grade | 1.17% | 3.12% | 0.046% |
| Concentrate grade | 9.43% | 24.95% | 0.36% |
| Recovery rate | 77.37% | 76.77% | 75.13% |
What are tantalum and niobium used for?
Due to their unique properties, tantalum and niobium have a wide range of high-end industrial applications.
What are the uses of tantalum (Ta)?
Electronics: The capacitor industry is the largest market for tantalum. Approximately two-thirds of tantalum powder and wire are utilized in the production of electronic capacitors, including those found in cell phones, computers, automobiles, and consumer electronics.
Aerospace: Tantalum metal finds application in aerospace industries, particularly for manufacturing high-temperature and corrosion-resistant components used in rockets, aircrafts, and missile systems.
Medical devices: Tantalum possesses biocompatibility and resistance to bodily fluids which makes it valuable in the medical field. It is employed in medical implants and devices such as pacemakers and orthopedic implants.
Chemical industry: Tantalum’s resistance to acid corrosion renders it highly valuable within the chemical industry. It can be utilized for creating evaporation vessels, electron tube electrodes, rectifiers, as well as handling corrosive chemicals.
What are the uses of niobium (Nb)?
Steel industry: Approximately 80% of the world’s niobium production is utilized for manufacturing high-strength low-alloy steel (HSLA), which finds applications in construction, automotive, and infrastructure projects.
Superconductor: Another significant application of niobium metal lies in the production of superconducting materials. Currently, Nb-Ti alloy stands as the most widely used and employed superconducting material.
Jewelry production: Niobium possesses unique surface properties that allow easy anodization to create vibrant surface coatings. This feature makes it popular for producing hypoallergenic jewelry.
Aerospace and electronics: In aerospace and electronics, niobium shares similarities with tantalum. Both metals are employed in capacitor production, as well as for creating superalloys and high-temperature alloys.
Medical devices: Tantalum exhibits biocompatibility and resistance to bodily fluids within the medical industry. It is extensively used in medical implants and devices such as pacemakers and orthopedic implants.
Chemical industry: Tantalum holds great value within the chemical industry due to its resistance against acid corrosion. It can be utilized for manufacturing evaporation vessels, electron tube electrodes, rectifiers, as well as handling corrosive chemicals.

