The shaking table is a machine that uses mechanical vibration and water washing to separate granular materials based on density.
In gravity separation, the shaking table (also known as gravity concentrating table) is widely used and efficient for sorting fine ore.
Shaking table beneficiation can be used as an independent method or combined with other methods such as jigging, flotation separation, magnetic separation, centrifugal concentrator, spiral classifier, spiral chute, and other beneficiation equipment.
What does shaking table mineral processing involve?
The shaking table is mainly used for separating and recovering gold, iron, manganese,copper, chromium,tungsten,molybdenum,tin,tantalum,nioium,and other rare metals and precious metal ores.

In addition, it can separate coal and purify non-metallic minerals like talc, limestone, garnet, and pyrophyllite. It can also process nonferrous ores before flotation separation.
Ftmmachinery Shaking Table is used for roughing, concentration, and sweeping to separate coarse sand (2-0.5 mm), fine sand (0.5-0.074 mm), sludge (within 0.074 mm), and other particle sizes. It is highly effective for selecting fine-grained materials below 1 mm, especially below 0.1 mm.
How does a shaking table work?
The shaking table carries out the beneficiation process on an inclined bed with riveted strips. It resembles a vibrating table that separates valuable minerals from waste minerals by moving back and forth.
Shaking table mechanism:
Material flows from the feeding chute to the bed surface where it gets loosened and stratified by water flow and bed surface vibration in longitudinal grooves.
Light mineral particles in the upper layer experience significant impact force and mostly move downward along the bed surface to become tailings. This side of the bed surface is referred to as the tailings side.
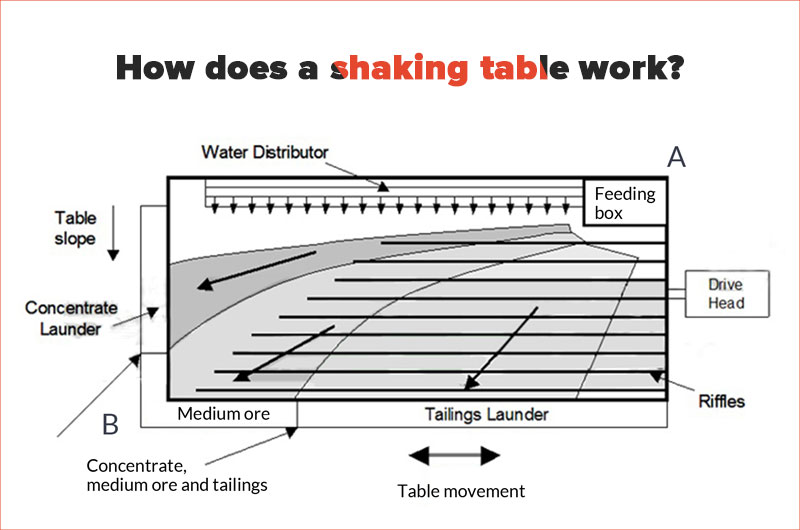
The dense mineral particles at the bottom of the bed move lengthwise due to differential movement of the bed surface and are discharged from the opposite end of transmission as concentrate. This specific location on the bed surface is referred to as the concentrate end.
The horizontal and longitudinal behaviors of mineral particles with varying densities and sizes differ on the bed surface. Eventually, these materials spread out in a fan shape on the bed surface, allowing for various products with different qualities to be obtained.
Here is a video demonstrating goldwire recovery using a shaking table.
What is the structure of a shaking table?
The shaking table has three main parts: the bed surface, the drive head, and the frame or append framework. The crank-link transmission mechanism enables longitudinal reciprocating motion of the bed surface.
1. Bed surface
Unlike other bed surfaces on the market, Ftmmachinery Shaking Table is specifically designed to withstand harsh conditions in the mining industry. It consists of a steel frame wrapped with polyurethane glass fiber reinforced plastic (FRP), and it features a special wear-resistant layer on its working surface.
In terms of design along its length, there are multiple parallel bed strips or grooves present on the bed surface. Ftmmachinery Shaking Table offers three types of bed bars: rectangular for coarse sand, trapezoid for fine sand, and groove-shaped for sludge.
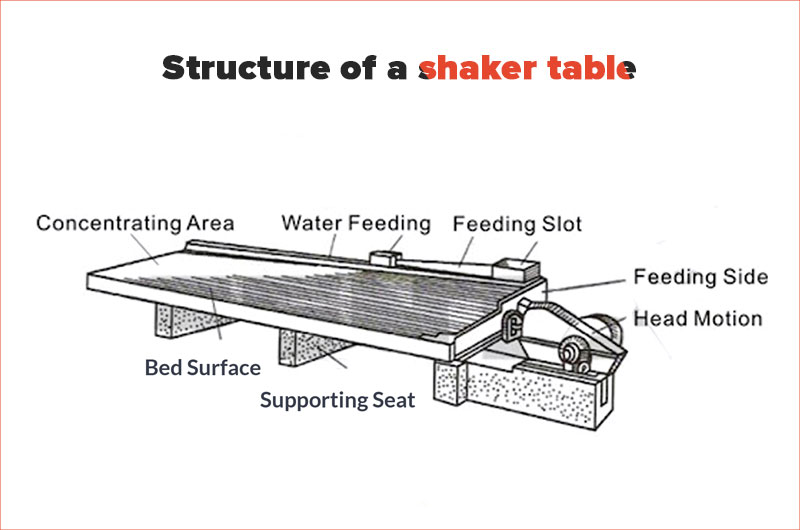
There is a feeding chute on the upper right side of the bed surface, which is about 1/3 to 1/4 of the total length. The feeding chute has many small holes to evenly distribute the slurry on the bed surface.
The flushing tank is connected to the feeding chute and accounts for 2/3 to 3/4 of the total length of the bed surface. Many small holes are made on one side of the tank to evenly feed flushing water along the longitudinal direction of the bed.
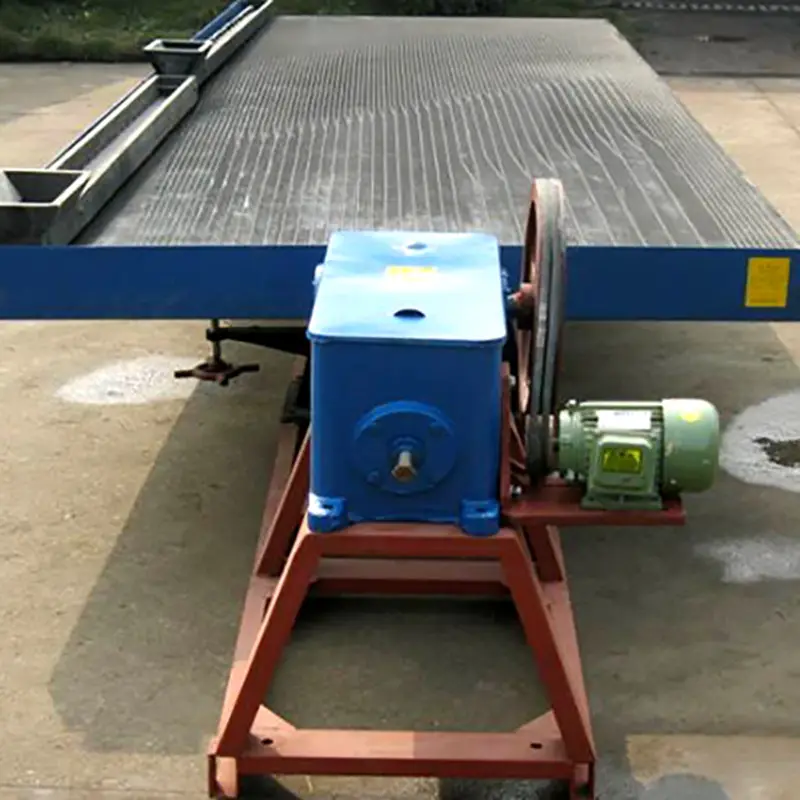
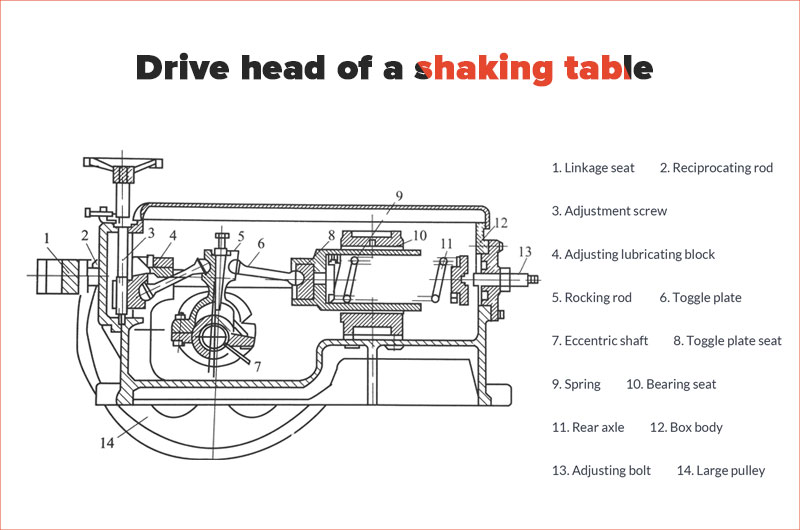
2. Drive head (Driving mechanism)
The shaking table’s drive head is powered by an electric motor and connected to the bed surface through a pull rod, causing asymmetric reciprocating motion along its longitudinal direction.
When advancing, the speed of the bed surface changes from slow to fast and then quickly stops.
When retreating, it rapidly accelerates from zero to maximum speed and then gradually decreases back down to zero.
3. Frame or attach a framework.
The support system for the bed surface can be categorized as either seated or suspension type.
Seated type means that the bed surface is directly connected to the bracket, and a slope adjustment device is installed on the bracket to adjust its lateral slope.
Suspension type refers to hanging the bed surface on the bracket using a wire rope. The bed surface is suspended in mid-air, and its slope can be adjusted by tightening or loosening the wire rope.
Ftmmachinery offers shaking tables for sale
For large and medium-sized gold processing plants, at least one large vibrating table is required, with prices starting from $500.
For small gold processing plants, a mini shaking table priced at $100 may suffice.
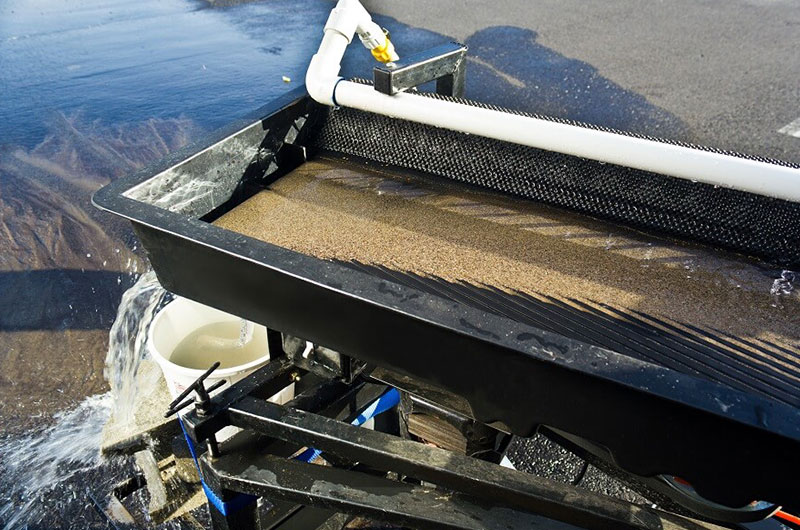


Separating precisely is its prominent advantage. We can obtain the final concentrate, medium ore, and tailings after the initial separation from the raw minerals.
The enrichment ratio (the ratio of concentrate grade to raw ore grade) is higher than many other mineral processing methods, exceeding 100 times.
Qualified concentrate and waste tailings can be obtained through a single separation process.
The ore forms a fan shape on the bed surface for easy observation and adjustment.
Compared to other vibrating tables in the market, Ftmmachinery Shaking Table utilizes a large strong channel steel frame (while other companies use small channel frames), wear-resistant FRP bed surface, Polypropylene materials feeding chute and collection chute (which other companies lack), as well as various grooves on the table.
It requires no chemicals and consumes minimal power.
How do you operate a shaking table?
There are several adjustments that need to be made before using the shaking table.
1. Adjusting the horizontal and longitudinal slope of the bed surface
Ensure that the table slope is sufficient and there is enough water flow. If the table is positioned too steeply or if there is excessive water spray, heavier particles will be swept over to the riffles.
| Types | Slope of coarse sand area | Slope of fine sand area | Slope of sludge area | Slope of bead surface |
| Installation of equipment | 1°~2° (lengthways) | 0.5°~1.0° | Basically no | 1.5°~5° (Tilt from the feeding side to the opposite side) |
| In actual operation | 2.5°~4.5° | 1.5°~3.5° | 1°~2° | 2 mm: 3. 5°~4° 0. 5 mm: 2. 5°~3. 5° 0. 1 mm: 2°~2.5° |
2. Feed Size
The effective recovery particle size is 2-0.02 mm. A vibrating table is used for coarse ore with a maximum feed particle size of 2 mm, fine ore with 0.5 mm, and slime with 0.074 mm.
3. Ore Feeding Amount
The amount of feeding ore depends on the granularity of the feed. If the ore grains are coarse, a large amount of feeding ore is required but excessive amounts can cause zoning problems. In such cases, adjusting the concentrate intercepting plate, increasing flushing water and horizontal slope of the shaking table surface is necessary.
4. Feed Concentration
In general, the feeding concentration for coarse-grained minerals is 20%-30% and for fine-grained minerals it’s 15%-25%.
When rapid rushing occurs on the shaking table bed surface, the ore concentration can be increased appropriately.
If there is a sand pile present, it’s necessary to reduce the ore concentration.
5. Shaking Table Bed Surface Partitioning
The bed surface of a shaking table consists of four areas: concentrating area, middle mine area, tailings area, and sludge area.
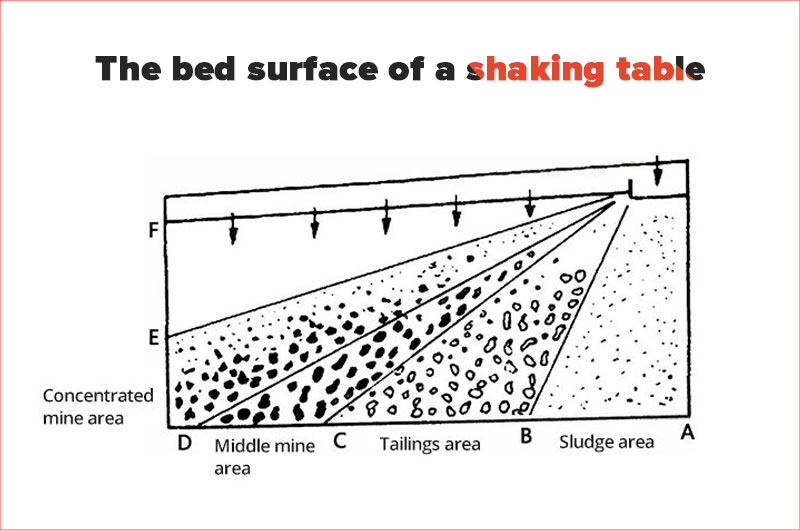
The sludge area is typically 0.9-1.4 m wide.
In the tailings area, the flow of ore should be stable without rapid rushing, and the ore bed must be submerged in water.
The middle mining area is used to separate the middle mine, primarily by adjusting the flushing water and lateral slope.
In the concentrating area, there should be clear separation of minerals with different specific gravities, so a stable and distinct boundary needs to be formed between the selected area and primary selection.
6. Flushing water
Flushing water includes feeding water and washing water.
During operation of the shaking table, if the concentrated zone becomes narrow and concentrate spills into medium-grade ore, reduce the amount of flushing water.
Conversely, if there are dry films on the surface of the shaking table, increase the amount of flushing water.
7. Stroke length and frequency
| Materials | Stroke | Times of stroke |
| Coarse grains in thick bed | Large | Small |
| Fine grains in thin bed | Small | Large |
GuogaoMachinery’s Shaking Table for Mineral Processing Plants
1. Gold Shaking Table
In Guinea, a 200 TPH gold ore processing plant primarily handles placer gold ore that mainly exists in particle form with a small clay content. To maximize the recovery of fine gold particles, GuogaoMachinery utilizes a combination of equipment including a trommel screen, jig, and shaking table.
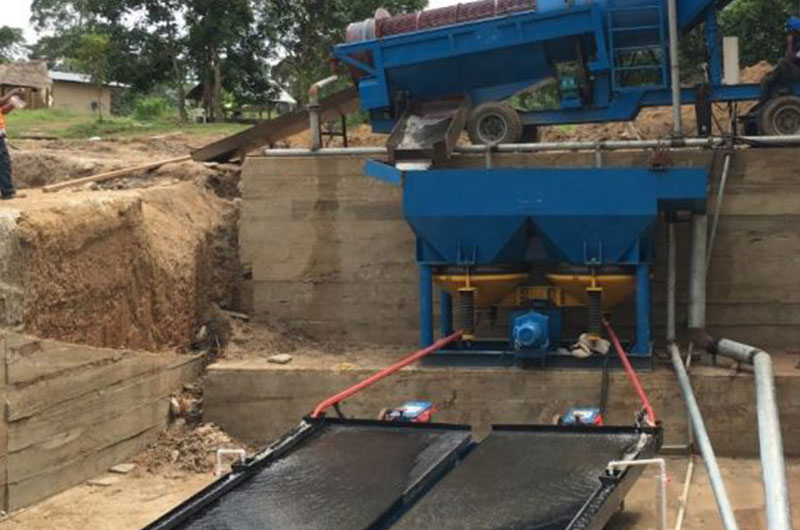

The raw ore is fed into the trommel screen to remove a small amount of clay. The gold-free gravel or stones are then separated and transported away by the belt conveyor.
A jig is used to collect gold particles or large gold nuggets ranging from 2-20 mm in size.
Next, the concentrate is processed on a shaking table. This helps effectively separate sand from the gold, as there may still be some sand present in the concentrate.
Shaking Table for chromite
In Zimbabwe, a certain lean chromite ore has a Cr2O3 content of only 8.19%. Ftmmachinery has conducted research on beneficiation technology and equipment for this type of lean chromite ore. After careful consideration, they have decided to adopt the beneficiation method: tail discharging through strong magnetic separation followed by full-grain separation using a shaking table. The results show relatively good indicators.
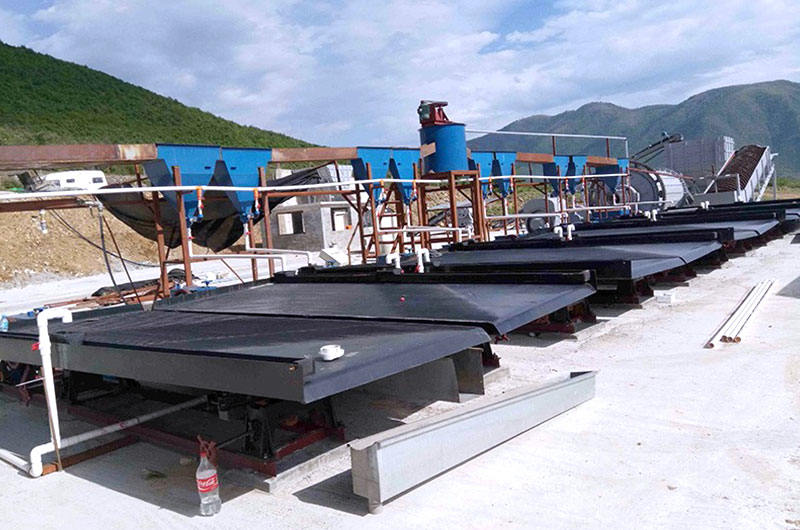

The first step is to crush and grind the chromite ore using a jaw crusher, cone crusher, ball mill, and other equipment until the grinding particle size reaches 60% at -200 mesh.
Next, employ Ftmmachinery Magnetic Separator for strong magnetic separation to eliminate qualified tailings with a yield of 50.21% and a tailing grade of only 2.19%. Consequently, this reduces the amount of ore entering the shaking table by half and significantly decreases the number of shaking tables required. Simultaneously, discarding the tail creates favorable conditions for sorting on the shaking table while further enhancing sorting efficiency.
Afterward, utilize a shaking table for selection in order to enhance chromite grade. Ultimately, achieve ideal indexes including concentrate grade of 39.98%, yield of 13.28%, chromium recovery rate of 64.74%, and SiO2 content of 4.07%.
| Model NO. | 6S | Tbele Size | 4520*1850*156mm | |
| Stroke | 8-36mm | Motor Power | 1.1kw | |
| Time/min | 240-380 | Dimension | 5630*1850*900mm | |
| Landscape | 0-5° | Table Weight | 650kg | |
| Material | Feeding Size | Mine Density | Flushing Water | Capacity(t/h) |
| Coarse Sand | 2-0.5mm | 10-30% | 0.5-3.5t/h | 1-2.5 |
| Fine Sand | 0.5-0.074mm | 0.8-1.2 | ||
| Ore Mud | 0.0774-0.037mm | 0.3-0.6 | ||







