Ilmenite is the primary source of titanium, which is widely utilized in various industries including metal production, paint manufacturing, paper production, plastic fabrication, textile manufacturing, and more.
This blog aims to provide an overview of the ilmenite beneficiation process and its associated processing plant.
Learn about ilmenite
Prior to beneficiation, a mineral test should be conducted to analyze the properties of the mineral. This can help minimize unnecessary equipment investment and achieve optimal beneficiation outcomes.
Ilmenite is a black iron-titanium oxide (FeTiO3) composed mainly of hematite, magnetite, pyrite, pyroxene, and amphibole. Ilmenite found in placer deposits often contains significant amounts of slime.
The Mohs scale hardness of ilmenite mineral is 5-6. It exhibits weak magnetic properties and has a granular, plate-like, flakey, and scaly structure.
The majority of ilmenite ores are extracted from heavy ore placer deposits. This particular type of ore does not require crushing or grinding prior to beneficiation; however, the slime must be washed using a trommel screen.

Ilmenite ores are also recovered from hard titanium rock ores that contain minerals like magnetite and feldspar. These ores need to be crushed (using a jaw crusher and cone crusher) and ground (using a ball mill) before beneficiation.
Ilmenite Beneficiation Process
Tests have shown that the most effective method for ilmenite beneficiation is a combination of gravity separation, magnetic separation, and flotation. This process can achieve an Ilmenite concentrate grade of 50% with a recovery rate of 80%.
The specific ilmenite beneficiation process depends on production requirements, ore properties, etc. Please watch this video on how to process ilmenite from hard rock.
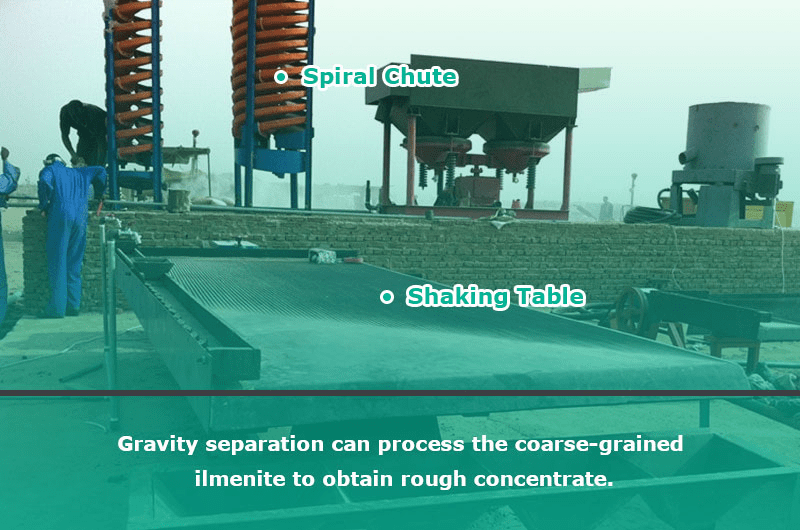
1.Gravity separation method
Gravity separation method can be used to process coarse-grained ilmenite (with a grade below 6%). It can undergo pretreatment or roughening to obtain a qualified rough concentrate with a grade of over 30%.
Gravity separation is a cost-effective and eco-friendly option, utilizing equipment such as the spiral chute and shaking table.
2.Magnetic separation method
Magnetic separation can remove iron and other magnetic minerals from ilmenite minerals. This method includes weak magnetic separation and strong magnetic separation. The weak magnetic separation is to separate titanomagnetite, while the strong magnetic separation is to discharge qualified tailings and prepare for the subsequent flotation process to obtain the final titanium concentrate.
The equipment is a magnetic separator. You can use a strong one for weak magnetic ilmenite, a medium one for vanadium titanomagnetite, and a weak one for placer-type ilmenite (containing magnetite).

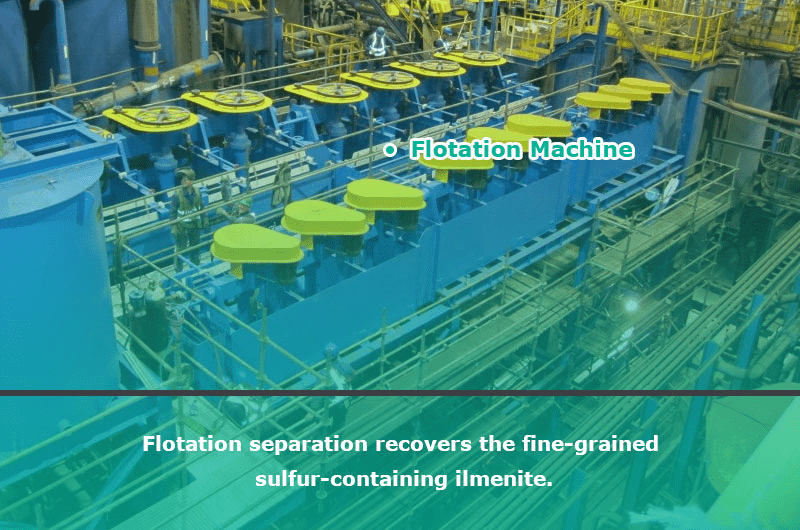
3. Flotation separation method
Flotation separation method mainly recovers the fine-grained sulfur-containing ilmenite by theflotation machine. The flotation of sulfide minerals is sorted first, followed by ilmenite flotation.
How do you use flotation reagents?
For sulfide flotation, the foaming agent used is No. 2 oil, the collector is xanthate, the activator is copper sulfate, and sulfuric acid is used as a pH adjuster.
For ilmenite flotation, H2SO4 is used as a pH adjuster. The collectors include oleic acid and its salts such as tar oil soap or a mixture of collectors and kerosene. Lead nitrate serves as an activator. Inhibitors like water glass, oxalic acid, sodium hexametaphosphate, carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC), etc., are also utilized.
Beneficiation of 4 common types of ilmenite ores

Ilmenite-magnetite: Utilize gravity-magnetic separation method. Coarsely discard the tails. Subsequently, grind and magnetically separate the ilmenite concentrate. If it contains sulfide, employ flotation method to first select sulfide, followed by fine-grained ilmenite selection.
Hematite-Ilmenite: Only select the mixed concentrate of ilmenite for beneficiation, then utilize fire smelting to obtain pig iron and high titanium slag.
Perovskite-titanomagnetite: Apply magnetic separation – flotation separation method. Use wet magnetic separation to select titanomagnetite. Then float calcite with a fatty acid collector and float ilmenite after removing intermediate ore.
Low-grade ultra-fine-grained ilmenite: The gangue primarily consists of titanium pyroxene and plagioclase, along with sulfide content. Employ gravity separation – magnetic separation – flotation – electric sepa
Ilmenite processing plant cases
10 TPH ilmenite processing plant in Australia
An Australian plant processes placer ore containing ilmenite. The primary titanium mineral in the ore is ilmenite, followed by rutile, white titanium, brookite, and sphene. Approximately 4.91% of the titanium is dispersed within iron-manganese minerals (goethite, pyrite, hydrohematite) and gangue minerals (kaolinite, quartz, feldspar).
Customer requirement: Titanium concentrate (TiO2) grade should be around 48%.
Guogao recommended solution:
Based on beneficiation tests conducted, the raw ore exhibits a high degree of monomer dissociation (up to 88.80%), allowing for direct gravity separation without the need for crushing and grinding.
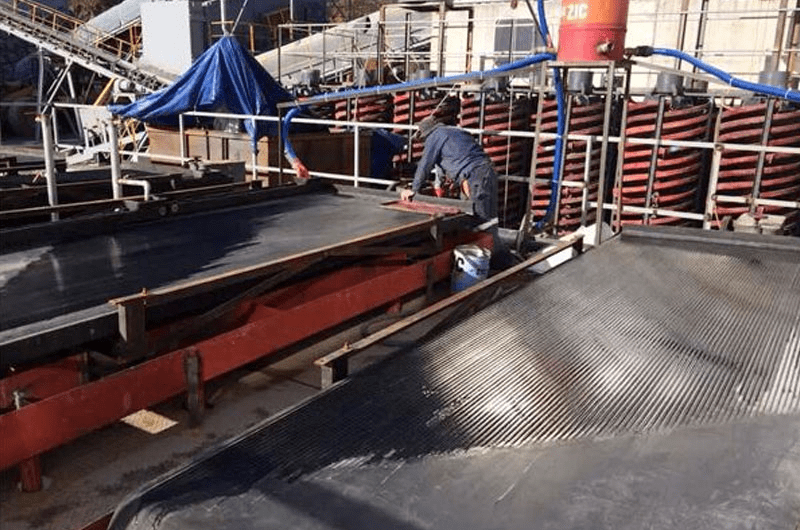

Ilmenite processing process:
- Screening and desliming: Utilize the trommel screen to wash away the slime. Discard the tailings with a yield of approximately 17.33% and the mud tailings with a yield of 40.81%. This will minimize the need for additional equipment and save costs.
- Rough selection: Employ the spiral chute for coarse selection and sweeping.
- Selection: The rough concentrate is fed into the 6-S shaking table for further selection and re-selection of medium-grade ore. Achieve a recovery rate of 75% for ilmenite concentrate.
40 TPH ilmenite processing plant in South Africa
The ilmenite found in South Africa is an inland placer with a low grade and high mud content. The main minerals containing titanium are ilmenite and titanomagnetite, along with small amounts of magnetite and hematite.
Customer requirement: To obtain a higher grade of ilmenite concentrate.
GUOGAO recommended solution:
The proposed process includes washing and desliming, gravity separation, grinding, magnetic separation, and another round of gravity separation. After washing, the loss rate of TiO2 in the slime is 22%. Following roughing, the TiO2 loss rate in rough tailings is 25%. After grinding, titanomagnetite and magnetite are initially separated using weak magnetic separation before being selected on the shaking table.
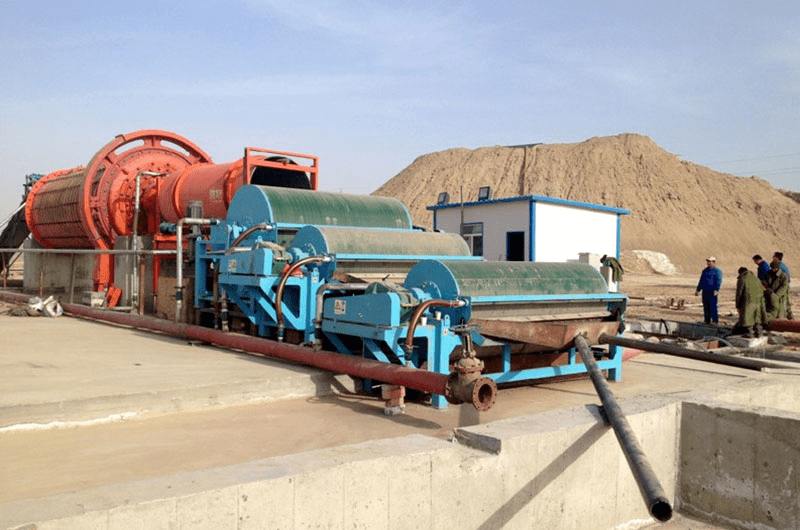

Ilmenite processing outcome:
The TiO2 recovery rate achieved 43.6%. Specifically, the ilmenite concentrate has a TiO2 grade of 46.5% with a recovery rate of 36.69%. The titanium magnetite concentrate yields 0.88%, with TFe grade at 56.89% and TiO2 content at 14.35%.

