Common types of gold ore mines:
Gold ore mines typically fall into four categories: placer gold mine, Carlin-type gold mine, volcanic gold mine, rock gold mine, and iron cap gold mine.

Types of Gold Mines:
Placer and rock gold mines are the most commonly mined:
After pretreatment, desilting, and ore washing, placer gold can be obtained through gravity separation.
Rock gold ores are crushed and ground into particles. Gold is extracted from these particles using various beneficiation methods.
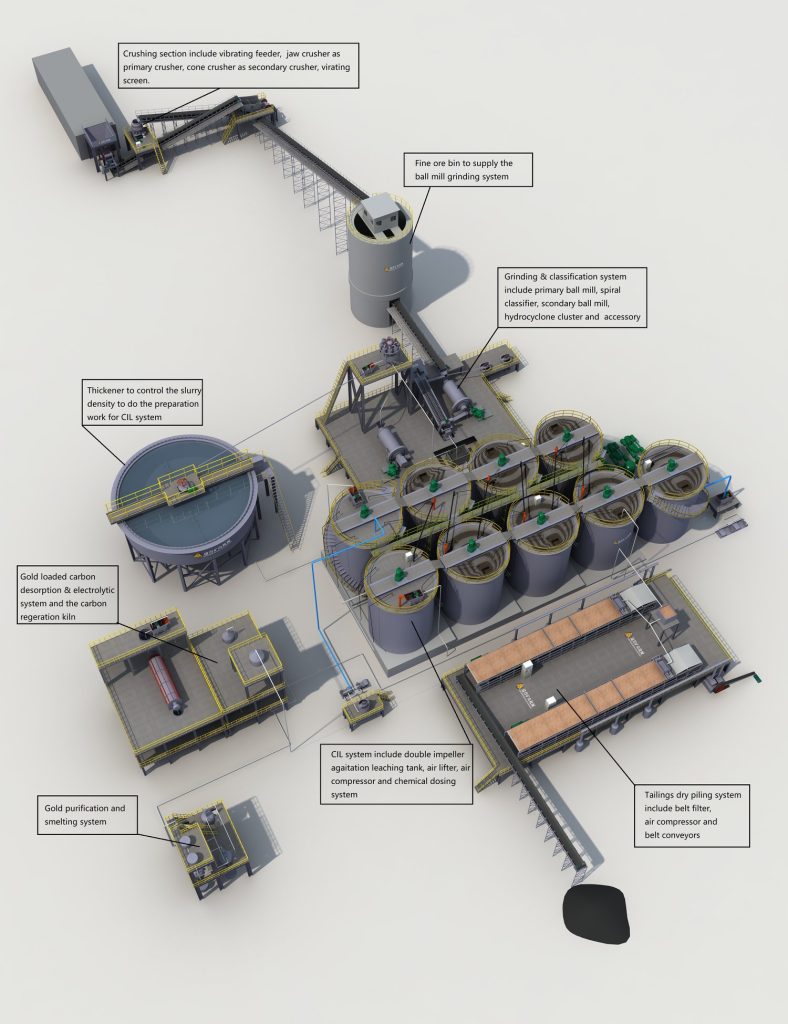
3 Stages of Gold Ore Processing:
Ⅰ. Crushing and screening stage
The crushing and screening stage in the industry consists of a three-stage process with closed-circuit operation. Gold ores undergo coarse, medium, and fine crushing to reduce them into smaller pieces. Screening equipment is used to separate properly sized ores for further processing.
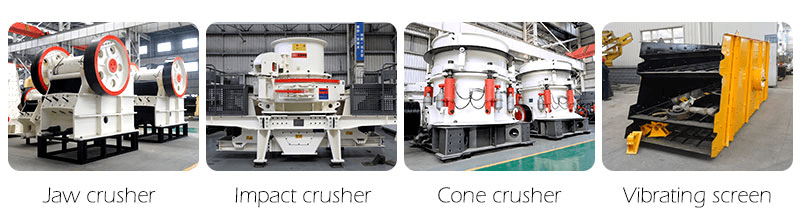
Different Types of Crushers for Gold Ore:
The equipment used in the crushing and screening stage includes jaw crusher, impact crusher, cone crusher, vibrating screen.
Ⅱ. Ore Grinding Stage
Grinding operations usually involve one or two ball mills with lattice or overflow types. The second stage grinding forms a closed circuit with a spiral classifier or hydrocyclone to achieve the desired fineness.
Grinding Stage:
Equipment used in the grinding stage includes ball mill and rod mill.

Ⅲ. Beneficiation Stage
The beneficiation stage is crucial for extracting gold throughout the entire processing plant. Placer and rock gold mines are processed extensively to extract concentrated amounts of gold.

Placer Gold Mine:
Gravity separation is ideal for processing placer gold ore due to its high particle content.
Rock Gold Mine:
Gravity separation or flotation separation may be chosen depending on specific composition factors.
Equipment used in the beneficiation stage includes magnetic separator,
spiral classifier,
flotation machine,
shaking table.

5 Methods of Gold Extraction:
Ⅰ.Cyanide Gold Process (Cyanidation):
This method involves several steps: finely ground ore is contacted with a cyanide solution, solid and clear solutions are separated, and gold is recovered from the solution using zinc powder precipitation.
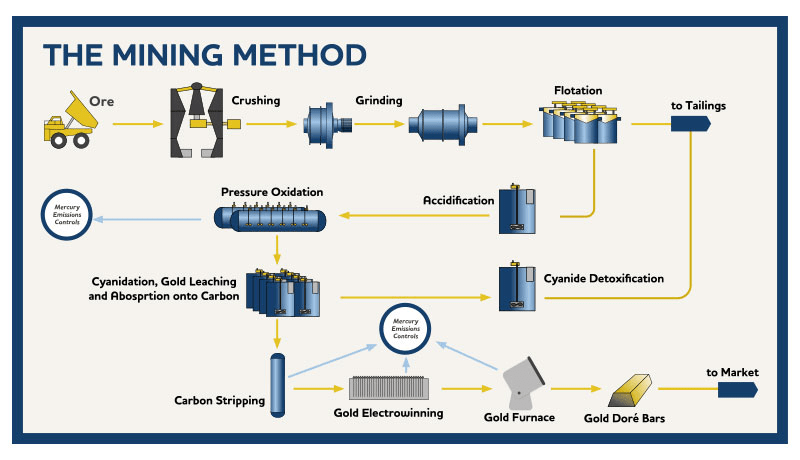
Cyanide Gold Process:
Applications:
Ag: Au > 5:1 in ore
Solid-liquid separation
Cyanidation of flotation concentrates
Two Types:
Stirring cyanide: used for tailings or complementing full mud cyanidation after gravity, mercury mixing, and flotation of gold concentrates.
Percolation cyanide: used for treating flotation tailings and heap leaching low-grade gold ore.
Ⅱ. Carbon Pulp Gold Extraction Process:
This process involves putting activated carbon into a cyanide ore slurry to adsorb dissolved gold onto the carbon. The gold is then extracted from the activated carbon.
Carbon Pulp Gold Process:
Applications:
Gold concretion process by flotation separation, tails from gravity separation, argillaceous gold oxide ore.
Large-scale beneficiation of raw gold ore with silver and copper content.
Oxidized ores with high slime content.
Benefits:
No need for solid-liquid separation equipment.
High gold recovery rate.
Activated carbon countercurrent adsorption achieves high adsorption rate.
Simplified leaching and adsorption process reduces infrastructure production costs.
Fast dissolution speed of high-recovery-rate gold ores.
Equipment required for carbon pulp mining includes leaching mixing tank,
activated carbon screen,
washing and thickening machine (two-layer or three-layer),
fast desorption electrolysis system,
high-frequency dewatering screen.
Comparison of CIP (Carbon-in-Pulp) and CIL (Carbon-in-Leach):
- CIP is more complex than CIL but has larger carbon storage capacity with lower concentration levels.
- Backlogged metal amount differs between CIP and CIL processes.
- In the CIP process, backlogged metal distribution in activated carbon matches that in solution; whereas in the CIL process, gold mainly accumulates on activated carbon with different distributions in carbon and solution.
- CIL process involves simultaneous immersion and adsorption, resulting in continuously increasing gold content in the solution.
- CIP process is a single adsorption process, leading to lower dissolved gold supplement and thus lower gold content compared to the CIL process.
Ⅲ.Resin Pulp Gold Extraction Process:
This method uses ion exchange resin to extract gold from ore pulp. Similar to carbon, solid spherical polystyrene resin beads are used instead of activated carbon grains for absorbing gold.
Resin Pulp Gold Process:
Application: Raw ore and concentrates.
Benefits:
Large adsorption capacity
Strong abrasion resistance of resin
No organic pollution
Easy desorption conditions for simple regeneration
Disadvantage: Poor selectivity in adsorption
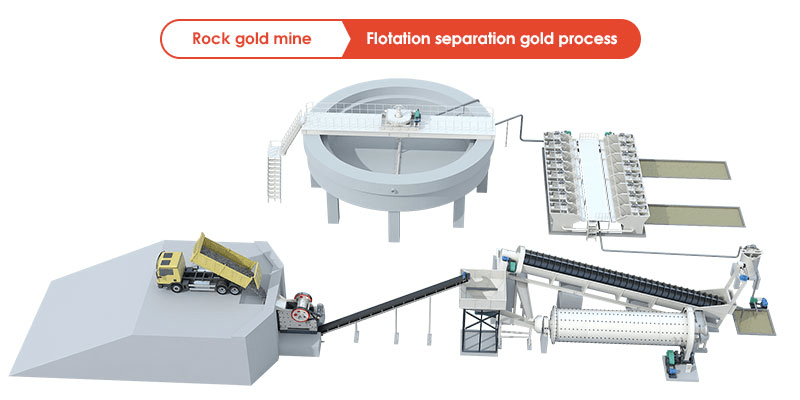
Ⅳ.Flotation Separation for Gold Extraction Process:
Flotation separation utilizes various reagents based on the physical and chemical properties of different types of gold ores. These reagents cause the attachment of gold particles to bubbles, which are then scraped off blades to obtain concentrate.
Flotation Separation Gold Process:
The process includes dosing,